Information for Health Professionals
This section includes information for health professionals involved in the DOLFIN trial, or who are interested in finding out more about the DOLFIN trial.
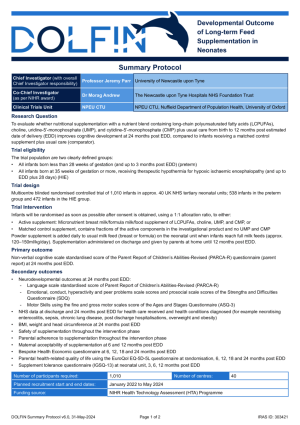
For full information about the DOLFIN trial, please see the trial protocol below:
Background
Nutrients docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) – a long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (LCPUFA), choline and Uridine-5-monophosphate (UMP) are particularly important for brain development and may improve neurodevelopmental outcomes. The Dolphin neonatal study ran from 2009 to 2013 in 3 UK Neonatal Units and aimed to investigate whether a micronutrient supplement containing long-chain fatty acids, choline and UMP improves neurodevelopment in neonates at risk for neurodevelopmental impairment. Results showed that the treatment group had higher mean cognitive scale scores and language scale scores on the Bayley Scales of Infant Development III compared to the placebo control group, indicating that a larger trial was warranted. In response to this and an NIHR commissioned call, the DOLFIN trial was set up.
Trial design
DOLFIN is a multicentre, blinded, randomised placebo-controlled phase III trial with an internal pilot and alongside economic evaluation.
The DOLFIN trial aims to evaluate whether nutritional supplementation with a nutrient blend containing long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFAs), choline, uridine-5'-Monophosphate (UMP), and cytidine-5'- monophosphate (CMP) plus usual care from birth to 12 months post estimated date of delivery (EDD) improves cognitive development at 24 months post EDD, compared to infants receiving a matched placebo supplement plus usual care (comparator).
Babies will be in one of two groups:
- Active supplement: Micronutrient breast milk/formula milk/food supplement containing LCPUFAs, choline, UMP, and CMP
or
- Matched placebo control supplement
The trial population will be stratified into two groups:
- Babies born less than 28 weeks of gestation (preterm group)
- Babies born at 35 weeks of gestation or more, receiving therapeutic hypothermia for hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy (HIE group)
The trial aims to recruit 1,010 babies (538 to the preterm group and 472 to the HIE group) from approximately 30 neonatal units across the UK.
Inclusion Criteria
- Preterm stratum: Infants born less than 28 weeks of gestation, up to discharge home from NNU or step-down site, and no more than 3 months post EDD
- HIE stratum: Infants born at 35 weeks of gestation or more, who have received therapeutic hypothermia for HIE, up to 40 weeks of gestation plus 28 days
- Individual with parental responsibility able to give consent.
- Parents able to comply with the protocol
- Infants likely to tolerate full enteral feeds
- Infant has realistic prospect of survival beyond discharge
Exclusion Criteria
- Middle Cerebral Artery infarcts
- Major congenital brain malformation, or genetic condition with abnormal brain development
- Infants with galactosaemia
- Infants receiving jejunal feeds
Primary outcome
Non-verbal Cognitive Scale standardised score of the Parent Report of Children's Abilities-Revised (PARCA-R)
Questionnaire (parent report) at age 24 months post EDD.
Secondary outcomes
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes at 24 months post EDD:
- Language scale standardised score of Parent Report of Children's Abilities-Revised (PARCA-R)
- Emotional, conduct, hyperactivity and peer problems scale scores and prosocial scale scores of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ)
- Motor Skills using the fine and gross motor scales score of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ-3)
- NHS data at discharge and 24 months post EDD for health care received and health conditions diagnosed (for example necrotising enterocolitis, sepsis, chronic lung disease, post discharge hospitalisations, overweight and obesity)
- Weight and head circumference at birth, and height, weight and head circumference at 24 months post EDD
- Safety of supplementation throughout the intervention phase
- Parental adherence to supplementation throughout the intervention phase
- Maternal acceptability of supplementation at 6 and 12 months post EDD
- Bespoke Health Economic questionnaire at 6, 12, 18 and 24 months post EDD
- Parental health-related quality of life using the EuroQol EQ-5D-5L questionnaire at randomisation, 6, 12, 18 and 24 months post EDD
- Supplement tolerance questionnaire (IGSQ-13) at neonatal unit, 3, 6, 12 months post EDD